When you test your autosomal DNA at any of the five genealogy DNA testing companies (ie. Ancestry, 23andMe, MyHeritage, Family Tree DNA, Living DNA), your X-chromosome is also examined and X-DNA is included in your raw data file and your DNA match segment information.
When you share X-DNA with a match, the unique inheritance pattern of X-chromosomes can help limit the search for your common ancestor to particular lines of your ancestry.
Family Tree DNA‘s Family Finder test identifies X-Matches with people you already match via your autosomal DNA, and displays them in your match list (see below).
You can view the X-match segment detail for specific matches in the FTDNA chromosome browser, and download all chromosome browser segment data to Excel or other software or sites for further analysis if desired (eg. GEDmatch).
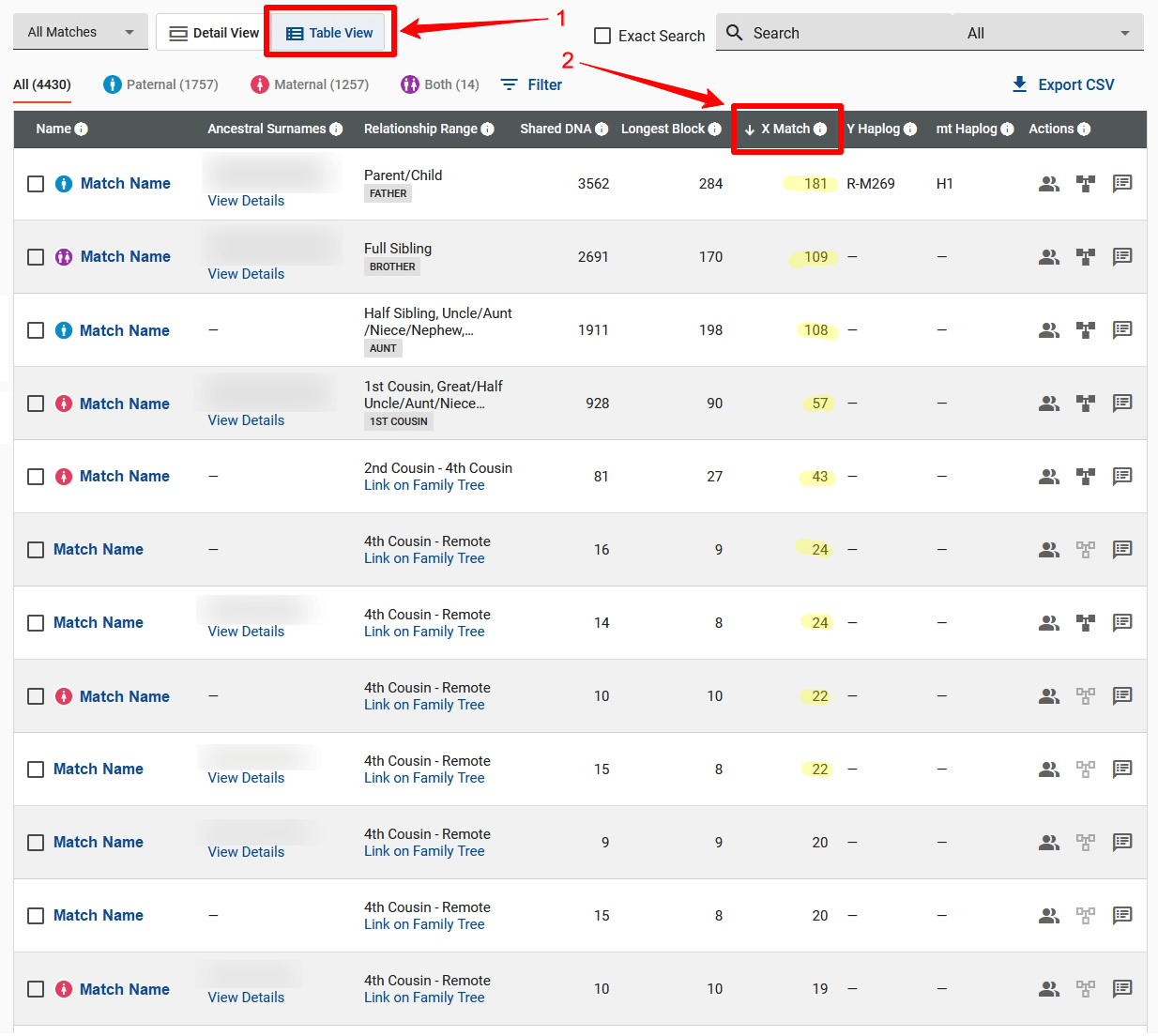
Your Family Finder default (Detail View) match list shows X-match information in the right-most column, although the quickest and easiest way to identify matches who share X-DNA with you is to switch to the Table View and then click on the X Match column heading to sort so that the highest X-matches appear at the top of the list, as per the example below:
23andMe X-DNA can be viewed in the 23andMe chromosome browser or downloaded, but only for those matches who choose to share genomes with you. The raw data can be transferred to GEDmatch for comparison with other kits in the GEDmatch database.
AncestryDNA does not provide or show any X-DNA information, so X-chromosome information can only be accessed by transferring a copy of the raw data to FTDNA or GEDmatch for analysis.
MyHeritage DNA does not yet show X-matches, but they announced at their Nov 2018 Live Conference that X-matches would be coming at some stage in future. You can upload a copy of your MyHeritage DNA raw data to FTDNA or GEDmatch for X analysis.
Living DNA does not yet report on X-matches, but will likely do so in the future when all their matching and features have been fully implemented. You can upload a copy of your Living DNA data to GEDmatch for X analysis.
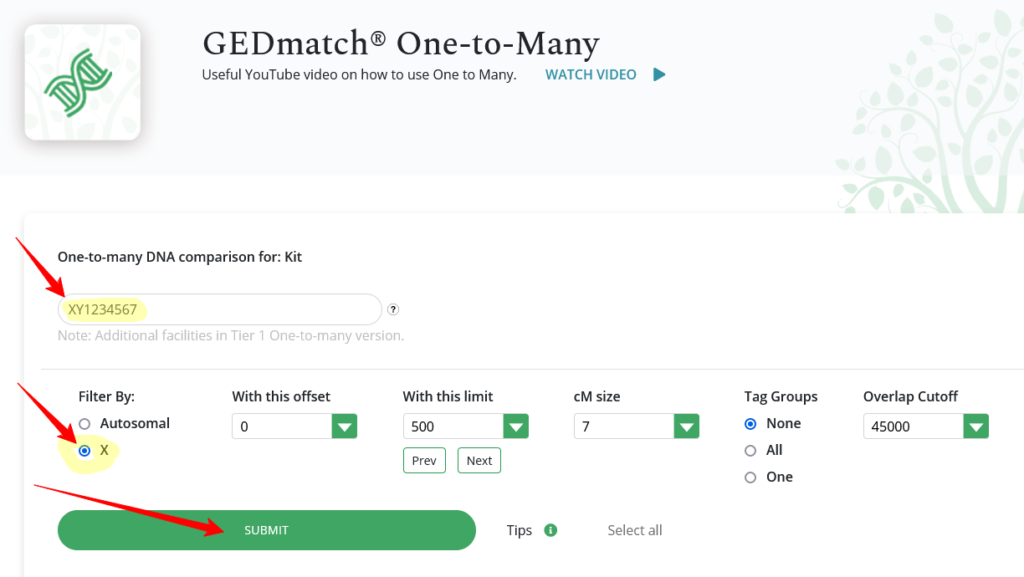
GEDmatch’s One-to-Many report can be used to identify your X-matches.
Select either the One-to-Many Limited Version tool from the Free Tools menu or the One-to-Many Full Version from the Tier 1 menu (for Tier 1 subscribers), enter your GEDmatch kit number, select to Filter by: X (as highlighted in the image below) and click Submit:
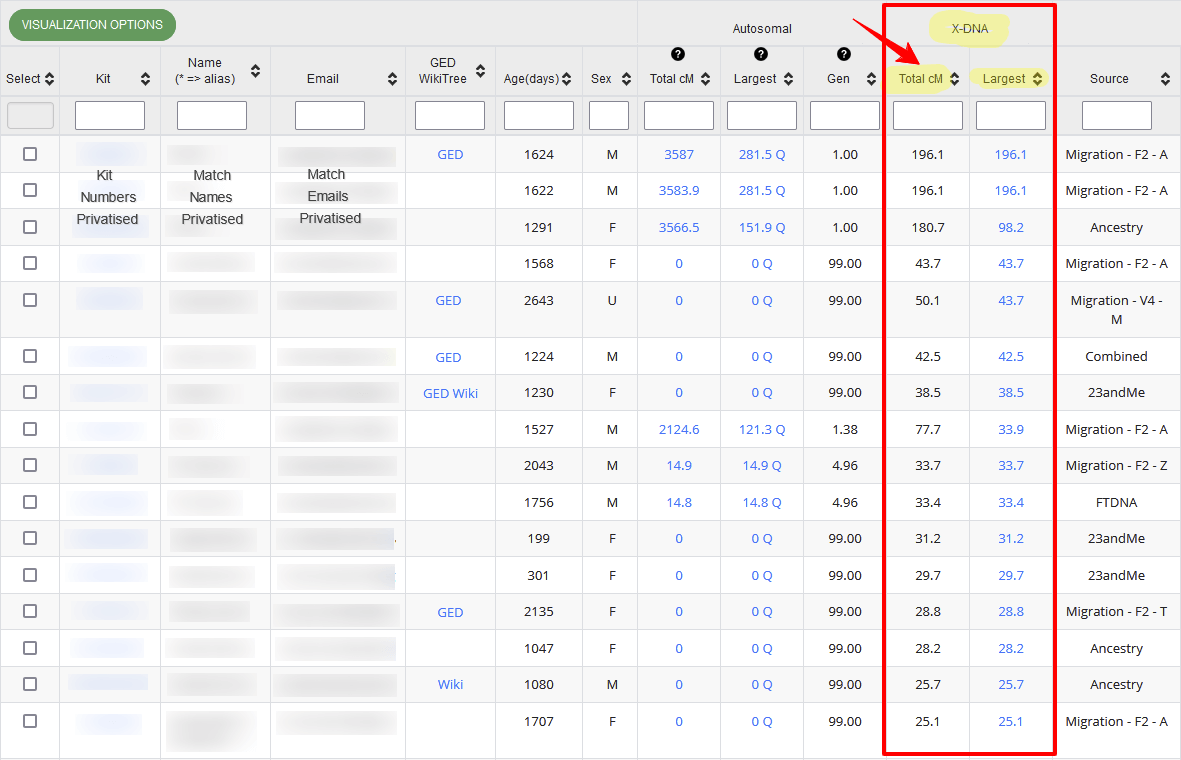
The resulting One-to-Many matches report will be sorted to show your highest-sharing X-DNA matches at the top of the list.
You can click any column headings to sort the match list, in ascending or descending order. Compare the results when you sort the X-DNA column by Total cM vs Largest Segment. (Note: to save space and make it easier to read, I omitted the Type, Haplogroups and Overlap columns from the image below).
In the example below, you’ll notice there are some matches who share quite large amounts of X-DNA (eg. 43.7cM, 50.1cM) but who share no Autosomal DNA. This is not uncommon and you may find you have some X-only matches that could be worth exploring.
Your sex is determined by the X and Y sex chromosomes: chromosome pair number 23.
Males inherit a Y chromosome from their fathers and an X chromosome from their mothers. So all their X-DNA is inherited from their mother.
Females inherit an X chromosome from their fathers, and an X chromosome from their mothers.
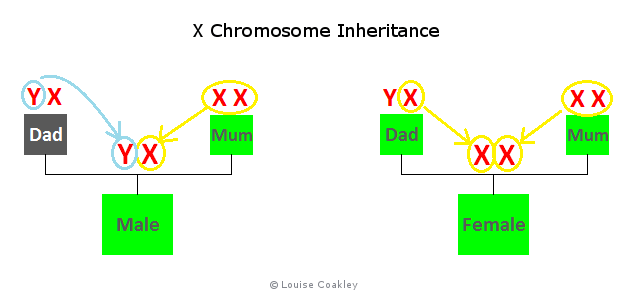
A mother contributes an X chromosome that is usually a recombined mix of both of her X chromosomes (but not always), and fathers contribute their whole X chromosome intact to their daughters.
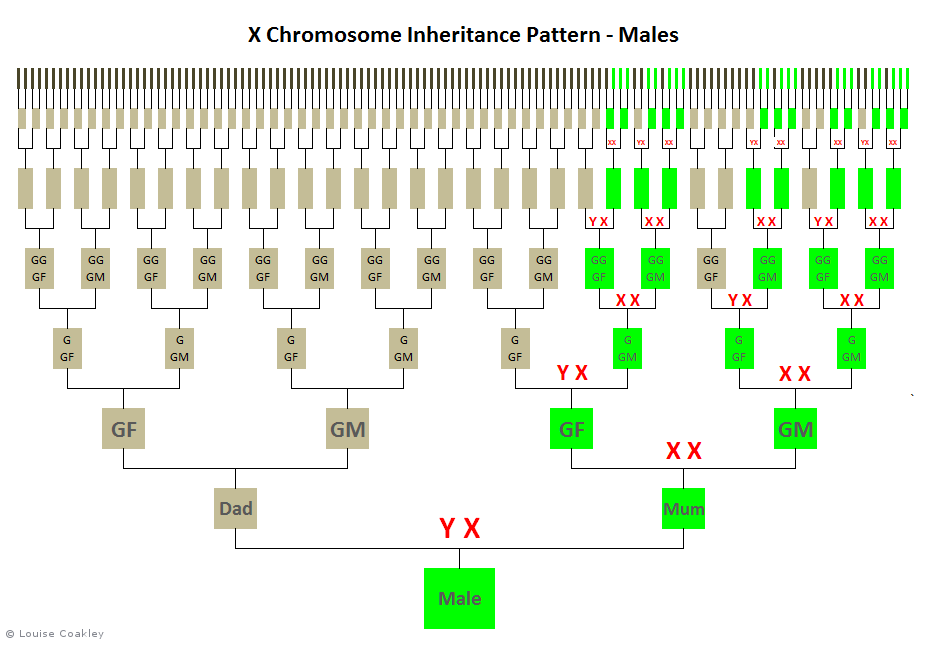
Because males only inherit an X chromosome from their mothers, if a male has an X-match in his DNA results, the shared ancestor must be on an ancestral line that follows the male X-inheritance pattern, as below (in green):
Because females inherit X chromosomes from both parents, if a female has an X-match in her DNA results, the shared ancestor must be on an ancestral line that follows the female X-inheritance pattern, as below (in green):
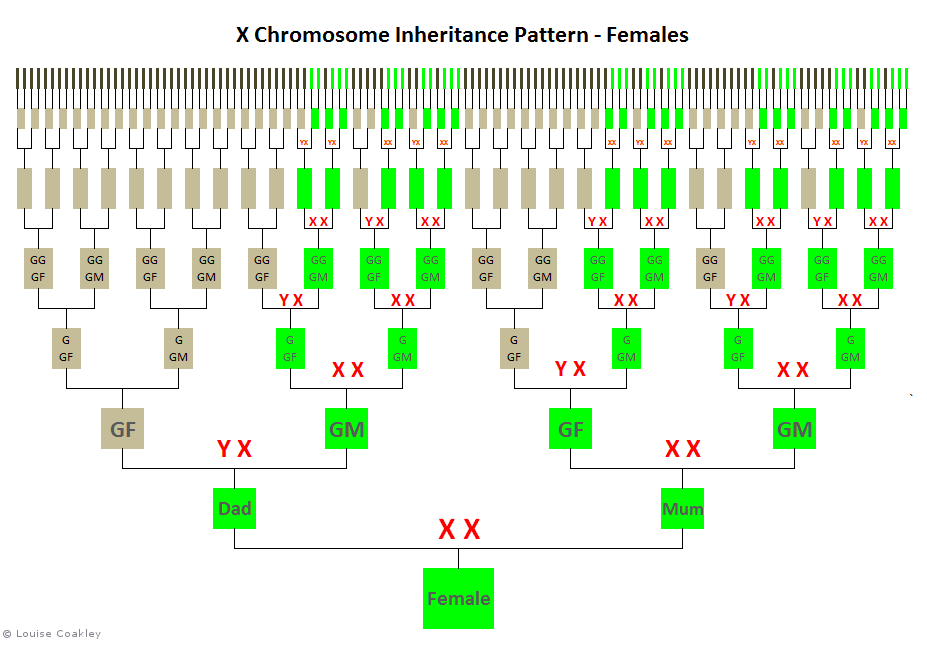
X-DNA cannot be passed down through two successive male generations.
Because some X-chromosomes pass down intact (through males) and skip a generation without recombining, and others are recombined (through females), the average expected percentage of shared X-DNA at each generation varies depending on the branch of the pedigree chart.
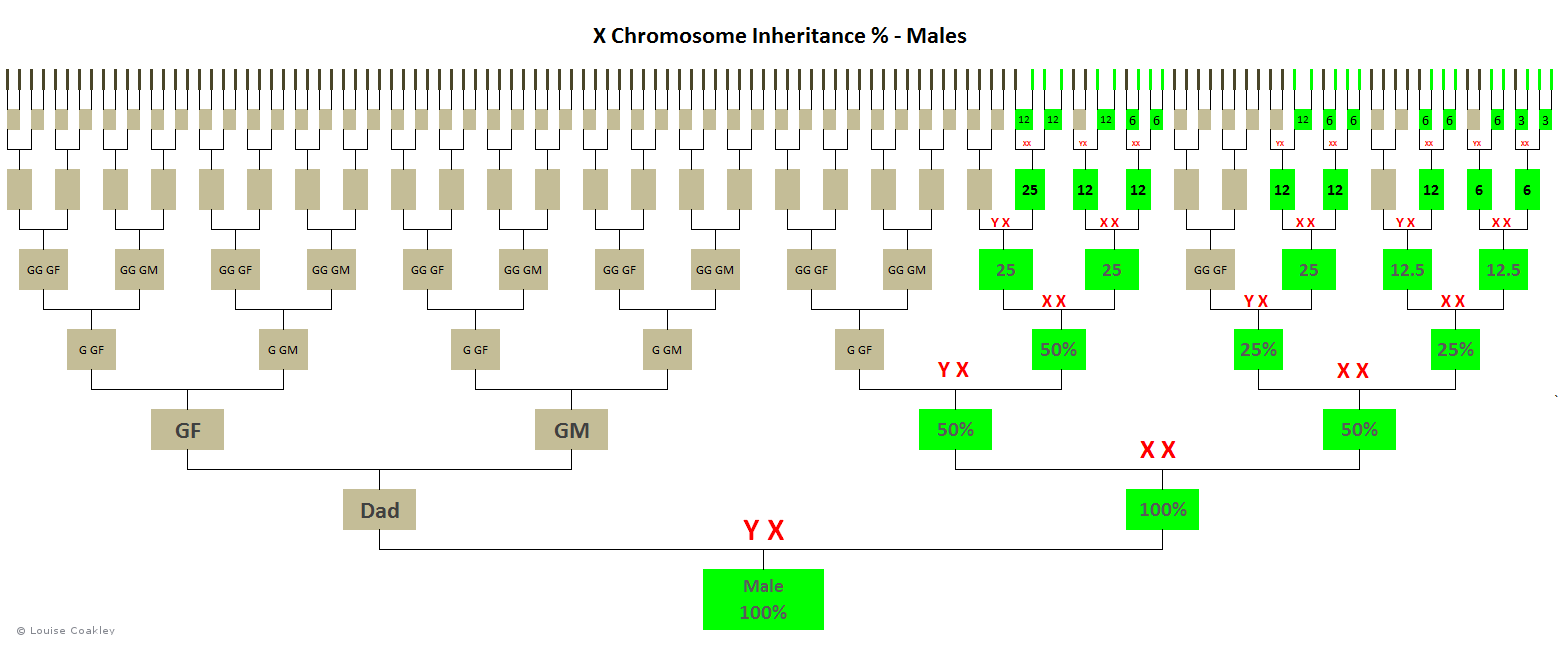
Compare the percentages across the same generations below.
For example, at the great-great-great-grandparent level, notice how the expected percentage of inherited X-DNA is only 3.1% on the far right direct maternal line, versus 12.5% on the left-most paternal line (and some other lines) at the same generation level.
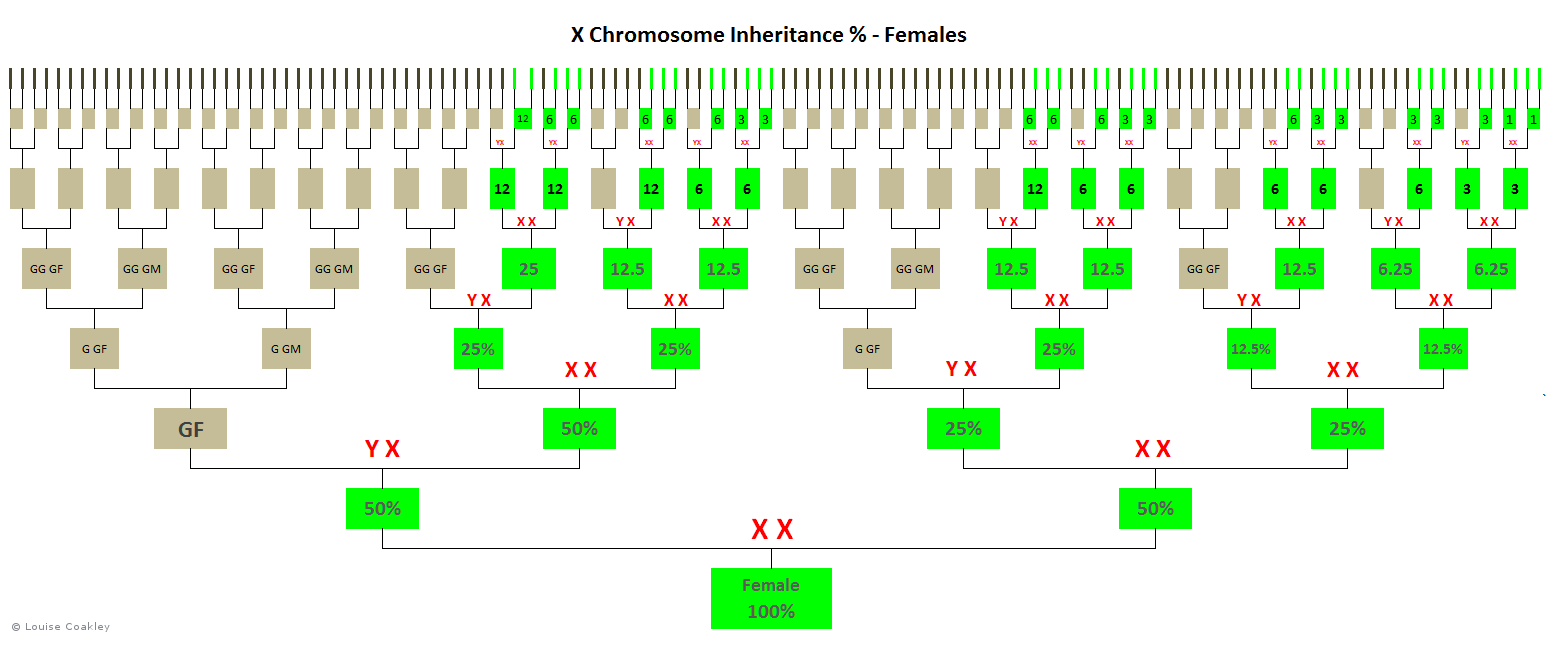
With no X-DNA inherited from some ancestors, varying amounts of X-DNA inherited from others, the randomness of DNA recombination at each generation, and occasional segments passed down intact over several generations, X-DNA can be quite unpredictable and it can be difficult to identify exactly where it came from.
It is common to share segments of X-DNA with people who share no significant amount of autosomal DNA.
Males generally get far fewer X-matches than females.
X-DNA’s best and most practical use is for isolating matches to particular family lines, even though the amount inherited cannot tell you from whom or how far back it came.
Nor can the absence of any X-DNA disprove your relationship (except for immediate family members – see below).
Focus on larger X-matches, such as 20cM or more, as smaller segments may not be reliable (or may just be too far back).
One very important point to understand in relation to X-DNA inheritance is that other than (1) paternal sisters (half or full), and (2) mothers and their children, you cannot exclude or rule out close relationships due to the absence of sharing X-DNA.
Full male-female siblings might not share any X-DNA, full brothers (same mother) might not share any maternal X-DNA, and your aunts and uncles and close cousins might not share any X-DNA with you. That is normal.
If using GEDmatch for X-DNA comparisons, use the Kit Diagnostic Tool to check that both kits being compared include SNP data for the X-chromosome, ie. Chromosome 23 (in case an incomplete or atDNA-only data file was uploaded from FTDNA, instead of the concatenated atDNA+X-DNA file).